India’s 2025 Heatwave Crisis: What You Need to Know
India is currently facing one of its most severe heatwaves in decades, with temperatures soaring above 45°C in several regions. This unprecedented heat not only threatens public health but also poses serious challenges to agriculture and daily life. As climate change accelerates, these extreme weather events are becoming more frequent and intense, making it crucial for everyone to understand the causes, impacts, and ways to stay safe.
Historical Context: Heatwaves in India
India has experienced several deadly heatwaves over the last few decades, but the frequency and intensity have increased alarmingly. For example, the 2015 heatwave claimed over 2,500 lives, primarily in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. Similarly, in 2019, northern India faced record-breaking temperatures with major health impacts. The 2025 heatwave continues this troubling trend, marking it as one of the hottest years on record, highlighting the urgent need for climate resilience.
What is Causing the 2025 Heatwave?
The 2025 heatwave is the result of a complex mix of natural climate variability and human-induced climate change. Rising greenhouse gas emissions trap more heat in the atmosphere, leading to hotter days globally. In India, delayed monsoons and low rainfall have allowed heat to build up, especially in northern and central regions. The formation of a “heat dome”—a high-pressure system that traps hot air—has worsened the situation. Additionally, urban heat islands, where cities become hotter due to concrete and asphalt, have intensified local temperatures.
Regions Most Affected
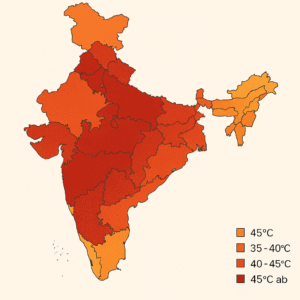
States like Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh are witnessing temperatures soaring beyond 45°C, with cities such as Jaipur, Delhi, and Lucknow experiencing prolonged heat spells. Southern states, including Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh, are also seeing above-average temperatures, making the heatwave truly nationwide. Rural areas, often with less access to cooling facilities, are especially vulnerable.
Impact on Health
Heatwaves pose severe health risks. Heat-related illnesses such as heatstroke, dehydration, and exhaustion are on the rise, especially among the elderly, children, outdoor laborers, and those with pre-existing conditions. Hospitals in affected areas report surges in emergency cases during peak heat periods. Mental health is also impacted, with increased stress and fatigue reported. The lack of awareness and preventive measures can lead to fatal outcomes. Public health officials and campaigns, like those outlined by the World Health Organization, emphasize the importance of hydration, avoiding peak heat hours, and recognizing symptoms early.
Effect on Agriculture and Economy
Agriculture, which employs a significant portion of India’s population, is hit hard by extreme heat. Crops such as wheat, rice, and pulses face heat stress, resulting in reduced yields. Farmers report damage to irrigation systems and soil moisture depletion, worsening drought conditions in some areas. These agricultural losses affect food security and rural incomes, potentially driving inflation in food prices nationwide. The economic toll of the heatwave extends beyond farming, impacting productivity in various sectors. Reports from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) highlight similar impacts worldwide and the urgency for climate-resilient farming methods.
Government Policies and Community Response
The Indian government and state authorities have implemented heat action plans to combat the crisis. These include issuing heat alerts, setting up cooling centers, and distributing water in vulnerable regions. Public health campaigns aim to raise awareness about heat safety, like those described by the Ministry of Earth Sciences. Additionally, some states are investing in long-term solutions such as urban greening to reduce the urban heat island effect and improving water management. Community volunteers and NGOs also play a crucial role in assisting at-risk populations by distributing water and checking on the elderly. You can learn more about heat safety and prevention in our heat safety tips post.
A Global Perspective: India and the World
Heatwaves are a global phenomenon linked to climate change. Countries in Europe, the US, and Australia have faced record-breaking temperatures and wildfires in recent years. India’s 2025 heatwave fits this pattern, underscoring the need for global cooperation on climate action. Reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Chan ge (IPCC) provide detailed scientific insights into how climate change is increasing heatwave frequency and severity worldwide. Understanding India’s experience can offer lessons on adaptation and mitigation strategies globally.
Tips to Cope with Extreme Heat
To stay safe during this heatwave, follow these important tips:
-
- Avoid outdoor activities between 11 AM and 4 PM, when heat is strongest.
-
- Drink plenty of water regularly, even if you don’t feel thirsty.
-
- Wear loose, light-colored, breathable clothing and a wide-brimmed hat.
-
- Use fans or air conditioning where possible; consider wet towels or cold packs.
-
- Eat light meals; avoid caffeine and alcohol which dehydrate the body.
-
- Check on elderly neighbors and family members frequently.
-
- Keep homes cool by closing curtains during the day and ventilating in the evening.
-
- Be aware of heat illness symptoms like dizziness, headaches, and nausea, and seek immediate medical help if needed.
For more detailed advice, see our full heat safety tips article.
Conclusion
With climate change driving more frequent and intense heatwaves, India faces a growing challenge to protect its people, economy, and environment. This 2025 heatwave serves as a stark reminder of the urgent need for climate resilience and proactive measures. By staying informed, prepared, and united, India can reduce the devastating impacts of extreme heat and safeguard its future.